Cartilage Definition Biology - Cartilage is the connective tissue that forms the skeleton of the mammalian embryos before the formation of the bone begins. The rectus sheath is a multilayered aponeurosis a fibrous sheath of dense regular connective tissue.
4 3 Connective Tissue Supports And Protects Anatomy And Physiology
Synovium is connective tissue that lines the structures in the bodys joints and a tendon sheath is a type of synovium that specifically lines tendons.

. The six types of synovial joints allow the body to move in a variety of ways. Types of Connective Tissues. Supporting the trachea is a ring of connective tissue called hyaline cartilage.
It covers the anterior and posterior surfaces of the upper three-quarters of the rectus abdominis muscle and the lower quarter of its anterior surface. In addition they perform the work of connecting the body tissue cell and organs. Joint examination begins with inspection for deformities erythema swelling or effusion and then proceeds to palpation for joint effusions warmth and point tenderness.
And persisting in the part of the human skeleton in adulthood. In fetal muscle endomysium is not always clearly defined so it is best to use the trichrome-stained slide slide 59-3 to this - it is the connective tissue immediately surrounding the individual cells and very delicate perhaps visible only as a bluish. Ligament most commonly refers to a band of dense regular connective tissue bundles made of collagenous fibers with bundles protected by dense irregular connective tissue sheaths.
Structure A tendon sheath is quite thin but it is composed of a few layers of connective tissuefibrous and synovial layers. Connective tissue is one of the many basic types of animal tissue along with epithelial tissue muscle tissue and nervous tissueIn embryology it develops from the mesodermConnective tissue is found in between other tissues everywhere in the body including the nervous systemThe three outer membranes the meninges that envelop the brain and spinal cord are composed of. Synovial joints are subdivided based on the shapes of the articulating surfaces of the bones that form each joint.
Ligaments connect bones to other bones to form joints while tendons connect bone to muscleSome ligaments limit the mobility of articulations or prevent certain movements. Musculoskeletal examination should start by distinguishing articular from periarticular or other connective tissue or muscular tenderness. Types of Synovial Joints.
However the rectus sheath doesnt completely enclose its contents. It is the only component of the skeleton found in some of the certain primitive vertrbrates including sharks and lampreys. Hyaline cartilage 100x Adipose tissue.
Connective tissue is one of the basic animal tissue. The six types of synovial joints are pivot hinge condyloid saddle plane and ball-and socket-joints Figure 943Figure 943 Types of Synovial Joints. Endomysium - thin connective tissue sheath consisting of basal lamina some reticular fibers and capillaries around each muscle fiber.
This slide showing a cross section of the mammalian trachea wind pipe contains examples of several different kinds of tissues. There are seven types of connective tissues found in the body of people.

Tissues Chapter 5 Connective Tissues A General Characteristics 1 Connective Tissues Bind Supp Smooth Muscle Tissue Loose Connective Tissue Serous Membrane
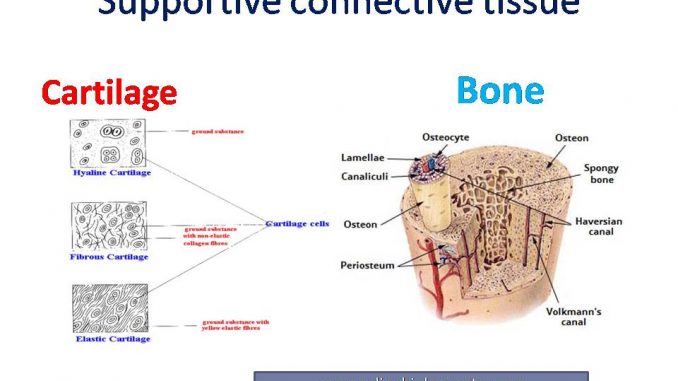
Supportive Connective Tissue Cartilage And Bone Online Biology Notes
4 3 Connective Tissue Supports And Protects Anatomy And Physiology
0 Comments